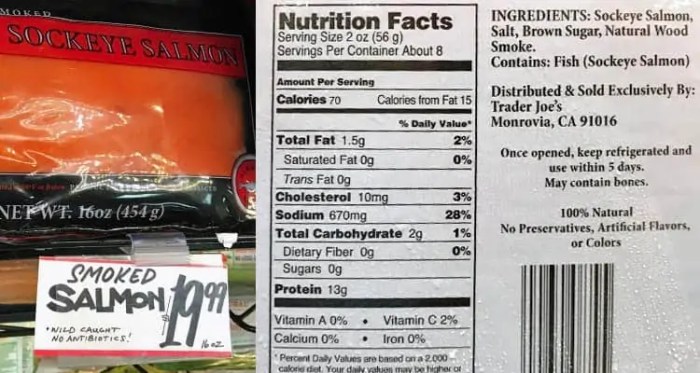
Nutritional Profile of Smoked Salmon: Smoke Salmon Nutrition Facts

Smoke salmon nutrition facts – Smoked salmon is a popular delicacy known for its rich flavor and nutritional benefits. Understanding its nutritional profile can help consumers make informed dietary choices. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the macronutrients and micronutrients found in a typical serving, along with a comparison of different types of smoked salmon.
Macronutrient Composition of Smoked Salmon
The macronutrient content of smoked salmon varies slightly depending on the species, preparation method, and portion size. The following table provides an approximate breakdown for a 3-ounce (85-gram) serving of Atlantic salmon:
| Nutrient | Amount per Serving | % Daily Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | 20-25 grams | 40-50% | Excellent source of high-quality protein, essential for building and repairing tissues. |
| Fat | 8-12 grams | 12-18% | Primarily unsaturated fats, including beneficial omega-3 fatty acids. |
| Carbohydrates | 0-1 gram | 0-1% | Naturally low in carbohydrates, making it suitable for low-carb diets. |
Micronutrient Content of Smoked Salmon
Smoked salmon is a rich source of several essential vitamins and minerals. These contribute to various bodily functions and overall health.
The following micronutrients are significantly present in smoked salmon:
- Vitamin D: Important for bone health and immune function.
- Vitamin B12: Crucial for nerve function and red blood cell formation.
- Vitamin A: Supports vision, immune function, and cell growth.
- Selenium: An antioxidant that protects cells from damage.
- Potassium: Essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids (EPA and DHA): Known for their anti-inflammatory properties and benefits for heart health.
Nutritional Differences Between Smoked Salmon Types
The nutritional content of smoked salmon can vary depending on factors such as whether it’s wild-caught or farmed, and the specific species.
Smoke salmon offers a rich source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids, beneficial for heart health. However, its sodium content is a significant consideration. A comparison with the sugar content found in processed snacks, such as those detailed in the brainiac fruit snacks nutrition facts data, highlights the contrasting nutritional profiles. Ultimately, choosing smoke salmon over sugary snacks offers a healthier, albeit potentially saltier, option for consumers concerned about their diet.
| Characteristic | Wild-Caught Salmon | Farmed Salmon |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acid Content | Generally higher | Can be lower, depending on feed |
| Selenium Content | Often higher | Can vary depending on feed and water conditions |
| Contaminant Levels (e.g., PCBs) | Generally lower | Potential for higher levels depending on farming practices |
| Fat Content | Can vary by species and season | Can be manipulated through feed |
Health Benefits of Smoked Salmon Consumption
Smoked salmon offers a range of health benefits stemming from its rich nutritional profile. Its high concentration of omega-3 fatty acids, selenium, and vitamin D, among other micronutrients, contributes significantly to cardiovascular health, brain function, and overall well-being. However, it’s important to note that moderation is key, as smoked salmon is also relatively high in sodium and calories.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Impact on Cardiovascular Health and Brain Function
Omega-3 fatty acids, specifically EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are abundant in smoked salmon. These fatty acids play a crucial role in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. They help lower triglycerides, blood pressure, and the risk of blood clot formation. Furthermore, DHA is a vital structural component of brain cell membranes and is essential for optimal brain function, cognitive performance, and potentially reducing the risk of age-related cognitive decline.
Studies have shown a correlation between higher omega-3 intake and a reduced risk of heart disease and improved cognitive function. For example, the Mediterranean diet, rich in fatty fish like salmon, is often associated with lower rates of heart disease.
Selenium’s Role in Overall Health
Smoked salmon is a good source of selenium, a trace mineral with potent antioxidant properties. Selenium protects cells from damage caused by free radicals, contributing to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including certain cancers. It also plays a crucial role in thyroid hormone metabolism, ensuring proper thyroid function. Adequate selenium intake is vital for immune function and overall health.
Deficiencies in selenium can lead to various health problems, highlighting the importance of including selenium-rich foods like smoked salmon in a balanced diet.
Benefits of Vitamin D and Other Micronutrients in Smoked Salmon
Beyond omega-3s and selenium, smoked salmon provides other essential nutrients. Vitamin D, crucial for calcium absorption and bone health, is present in smoked salmon. Other micronutrients, including potassium, niacin, and vitamin B12, contribute to various bodily functions. Vitamin B12 is particularly important for nerve function and red blood cell production. The combined effect of these micronutrients contributes to overall health and well-being.
For instance, adequate vitamin D levels are linked to a reduced risk of osteoporosis and improved immune function.
Infographic: Key Health Benefits of Smoked Salmon, Smoke salmon nutrition facts
Imagine an infographic with a central image of a slice of smoked salmon. Surrounding this image are four distinct sections, each representing a key health benefit:* Section 1: Heart Health: This section features a stylized heart with icons representing lower blood pressure, reduced triglycerides, and decreased risk of blood clots. The accompanying text reads: “Omega-3 fatty acids in smoked salmon help lower blood pressure, reduce triglycerides, and decrease the risk of blood clots, promoting cardiovascular health.”* Section 2: Brain Boost: This section depicts a brain with synapses firing.
The text reads: “DHA, an omega-3 fatty acid, is crucial for brain cell function and cognitive performance, supporting healthy brain function and potentially reducing the risk of cognitive decline.”* Section 3: Antioxidant Power: This section shows a cell protected by a shield, representing selenium’s antioxidant effects. The text explains: “Selenium, a potent antioxidant, protects cells from damage, contributing to a reduced risk of chronic diseases.”* Section 4: Nutrient Rich: This section displays various icons representing Vitamin D, B12, Potassium and Niacin.
The text summarizes: “Smoked salmon is a good source of Vitamin D, B12, Potassium and Niacin, supporting bone health, nerve function, and overall well-being.”
Comparison with Other Protein Sources
Smoked salmon offers a unique nutritional profile compared to other popular protein sources. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed dietary choices based on individual needs and preferences. The following comparison highlights key nutritional aspects of smoked salmon alongside chicken breast, tuna, and tofu. Note that nutritional values can vary depending on preparation methods and specific brands.
| Protein Source | Protein (grams per 100g) | Fat (grams per 100g) | Calories (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoked Salmon | 20-25 | 10-15 | 180-220 |
| Chicken Breast (cooked) | 30-31 | 2-3 | 165-170 |
| Tuna (canned in water) | 25-30 | 1-2 | 120-130 |
| Tofu (firm) | 8-10 | 4-5 | 70-80 |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Smoked Salmon Compared to Alternatives
The table above illustrates that smoked salmon provides a good source of protein, but it’s higher in fat and calories than chicken breast or tuna. Tofu, on the other hand, is significantly lower in both protein and calories. The advantages of choosing smoked salmon lie in its rich omega-3 fatty acid content, vitamin D, and unique flavor profile.
These contribute to its potential health benefits, such as reduced inflammation and improved cardiovascular health. However, its higher fat and sodium content compared to leaner options like chicken breast or tuna should be considered, particularly for individuals managing weight or sodium intake. The lower protein content of tofu makes it less suitable as a primary protein source for individuals with high protein requirements.
Ultimately, the optimal choice depends on individual dietary needs and goals.
Helpful Answers
Is smoked salmon high in cholesterol?
No, smoked salmon is relatively low in cholesterol. The cholesterol content is usually overshadowed by the significant benefits of its omega-3 fatty acids.
Can I eat smoked salmon every day?
While it’s packed with nutrients, daily consumption might lead to excessive sodium intake. Aim for moderation and balance it with other protein sources.
How long can I keep smoked salmon in the fridge?
Store it properly sealed in the refrigerator for 3-5 days for optimal freshness and safety. Always check for any off-odors or unusual appearances before consumption.
Is smoked salmon suitable for pregnant women?
Yes, it can be a good source of omega-3s, but choose reputable brands and ensure it’s handled and stored correctly to minimize the risk of listeria.
