Nutritional Profile of Asian Pears

Asian pear nutrition facts – Asian pears, also known as nashi pears, offer a delightful sweetness and crisp texture, but their nutritional value extends far beyond their appealing taste. Understanding their nutritional profile can help you incorporate this fruit effectively into a balanced diet. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients found in this delicious and surprisingly healthy fruit.
Macronutrient Composition of Asian Pears
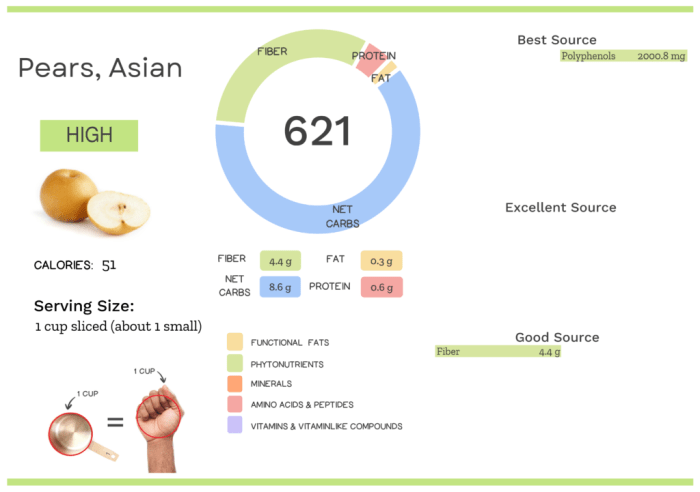
The macronutrient content of Asian pears primarily consists of carbohydrates, with minimal amounts of protein and fat. This makes them a relatively low-calorie fruit, ideal for those watching their weight. The following table provides a clearer picture, based on a typical serving size of one medium-sized Asian pear (approximately 180 grams):
| Nutrient | Amount per Serving (1 medium pear, ~180g) | % Daily Value (DV)* | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 28 grams | ~9% | Primarily in the form of natural sugars. |
| Sugar | 17 grams | N/A | Mostly fructose, glucose, and sucrose. |
| Fiber | 6 grams | ~24% | Contributes to digestive health. See below for details. |
| Protein | 0.5 grams | ~1% | Negligible protein content. |
| Fat | 0.1 grams | ~0% | Minimal fat content. |
Percent Daily Values are based on a 2,000 calorie diet. Individual needs may vary.
Vitamins and Minerals in Asian Pears and Their Health Benefits
Asian pears are a good source of several essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall health and well-being. These nutrients play vital roles in various bodily functions.
The following list highlights key vitamins and minerals found in Asian pears and their associated health benefits:
- Vitamin C: A potent antioxidant that supports the immune system and protects cells from damage. A single Asian pear contributes a significant portion of the daily recommended intake.
- Potassium: An essential mineral crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure and regulating fluid balance within the body. Potassium is vital for nerve and muscle function.
- Copper: Plays a critical role in energy production, iron metabolism, and the formation of connective tissues. Copper deficiencies can lead to various health issues.
- Vitamin K: Important for blood clotting and bone health. Vitamin K contributes to the synthesis of proteins necessary for these processes.
Fiber Content and Digestive Health
The significant fiber content in Asian pears is a key contributor to their positive impact on digestive health. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, promoting regularity and preventing constipation. Furthermore, soluble fiber, a type found in Asian pears, helps regulate blood sugar levels and lower cholesterol. The high fiber content contributes to a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management.
For example, individuals experiencing occasional constipation often find relief by incorporating foods rich in fiber, such as Asian pears, into their diet. This makes them a valuable addition to a healthy gut-friendly diet.
Health Benefits of Asian Pear Consumption
Asian pears, with their crisp texture and subtly sweet flavor, offer more than just a delightful taste experience. Packed with essential nutrients and boasting a compelling array of bioactive compounds, these fruits contribute significantly to overall health and well-being. Regular consumption can provide a range of benefits, impacting everything from cardiovascular health to immune function. Let’s delve into the specific ways Asian pears contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits of Asian Pears
Asian pears contribute to cardiovascular health primarily through their fiber and potassium content. The high fiber content helps regulate cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol in the digestive tract and promoting its excretion from the body. This can reduce the risk of high cholesterol, a major contributor to heart disease. Furthermore, the potassium in Asian pears helps to balance sodium levels, which is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure.
High blood pressure is another significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and by counteracting the effects of sodium, Asian pears contribute to a healthier cardiovascular system. Studies have shown a correlation between increased potassium intake and reduced risk of stroke. While more research is needed specifically on Asian pears and cardiovascular health, the existing evidence strongly suggests a beneficial role.
Asian Pears and Immune System Support, Asian pear nutrition facts
The immune-boosting properties of Asian pears stem from their rich vitamin C content. Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that plays a vital role in supporting the immune system’s function. It aids in the production of white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting off infections and diseases. Moreover, Asian pears contain other antioxidants, such as flavonoids, which further enhance the body’s defense mechanisms.
These compounds help neutralize harmful free radicals, reducing oxidative stress that can damage cells and weaken the immune system. A strong immune system is essential for overall health, and the combination of vitamin C and other antioxidants in Asian pears contributes to this crucial function. Imagine the effect of regularly incorporating these pears into your diet, bolstering your body’s natural defenses against illness.
Antioxidant Contribution to Overall Well-being
The antioxidants in Asian pears, including vitamin C and various flavonoids, are key contributors to overall well-being. Antioxidants combat oxidative stress, a process that involves the damage caused by free radicals. This damage can contribute to aging, chronic diseases, and inflammation. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants help protect cells from damage and reduce the risk of various health problems.
The antioxidants in Asian pears not only support immune function but also contribute to healthy skin, improved cognitive function, and reduced risk of chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease. Consider the cumulative effect of consuming foods rich in antioxidants like Asian pears—a gradual but significant improvement in your long-term health prospects.
Comparison of Asian Pear Nutritional Benefits with Other Common Fruits
While many fruits offer health benefits, Asian pears stand out in certain aspects. Compared to apples, Asian pears generally have a slightly lower calorie count and a higher water content, making them a refreshing and hydrating option. When compared to oranges, they offer a similar amount of Vitamin C, but with a different profile of other vitamins and minerals.
While Asian pears boast a delightful crunch and impressive fiber content, let’s not forget the equally nutritious world of other fruits! For a juicy comparison, one might consult the detailed nutritional breakdown of red grapes, readily available at nutrition facts red grapes , before returning to the subtle sweetness and vitamins found within our beloved Asian pear. Indeed, a balanced diet requires a diverse fruity portfolio!
Bananas, while rich in potassium, lack the same level of fiber found in Asian pears. The unique combination of nutrients in Asian pears, including fiber, potassium, and various antioxidants, sets them apart from other common fruits, offering a diverse range of health benefits. The best approach is to consume a variety of fruits to obtain a broad spectrum of nutrients.
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations: Asian Pear Nutrition Facts

While Asian pears offer a wealth of nutritional benefits, it’s crucial to acknowledge potential drawbacks and individual considerations to ensure safe and effective consumption. Understanding these factors allows you to maximize the positive impacts of incorporating Asian pears into your diet while minimizing any potential risks. This section will explore potential allergic reactions, the glycemic impact, and appropriate serving sizes.Asian pears are generally well-tolerated, but like any fruit, allergic reactions are possible, though relatively rare.
These reactions can range from mild symptoms like itching or hives to more severe, though less common, reactions such as anaphylaxis. Individuals with known allergies to other fruits, particularly those in the Rosaceae family (apples, pears, peaches, etc.), should exercise caution and potentially consult with an allergist before consuming Asian pears. Always start with a small quantity to assess your tolerance.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to Asian pears are not widespread, but they can occur. Symptoms can vary widely in severity, from mild skin reactions (itching, rash) to more serious reactions involving the respiratory system (difficulty breathing, wheezing) or digestive system (nausea, vomiting). Individuals with a history of fruit allergies should proceed with caution and possibly perform a small test portion before consuming a larger amount.
If any allergic reaction occurs, seek immediate medical attention.
Glycemic Index and Blood Sugar Management
The glycemic index (GI) of Asian pears is moderate, typically ranging from 30 to 50. This means they cause a relatively slow and gradual rise in blood sugar compared to foods with a high GI. However, the actual impact on blood sugar can vary based on factors such as ripeness, serving size, and individual metabolic responses. Individuals managing diabetes or other blood sugar conditions should monitor their blood glucose levels after consuming Asian pears and adjust their intake accordingly.
It’s advisable to incorporate Asian pears as part of a balanced meal, combining them with protein and healthy fats to help moderate the glycemic response. For example, pairing an Asian pear with a handful of almonds can help slow down the absorption of sugars.
Appropriate Serving Sizes
While Asian pears are nutritious, moderation is key. A typical serving size might be one medium-sized Asian pear (approximately 150-200 grams). Consuming excessive amounts could lead to potential digestive discomfort, particularly due to the high fiber content. Remember, individual needs vary based on factors such as age, activity level, and overall diet. It’s always best to listen to your body and adjust your serving size accordingly.
For instance, an athlete with high caloric needs might find a larger serving beneficial, whereas someone with specific dietary restrictions might opt for a smaller portion.
Questions Often Asked
Are Asian pears good for weight loss?
Asian pears are relatively low in calories and high in fiber, which can contribute to feelings of fullness and aid in weight management. However, they should be part of a balanced diet and exercise plan for effective weight loss.
Can I eat Asian pears if I have diabetes?
While Asian pears contain natural sugars, their glycemic index is moderate. Individuals with diabetes should consume them in moderation and monitor their blood sugar levels. Consulting a doctor or registered dietitian is recommended.
How should I store Asian pears to maintain their freshness?
Store Asian pears at room temperature until ripe. Once ripe, refrigerate them to slow down the ripening process and extend their shelf life.
Are there any known interactions between Asian pears and medications?
No significant interactions between Asian pears and medications have been reported. However, if you have concerns, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
