Nutritional Composition of Carrots
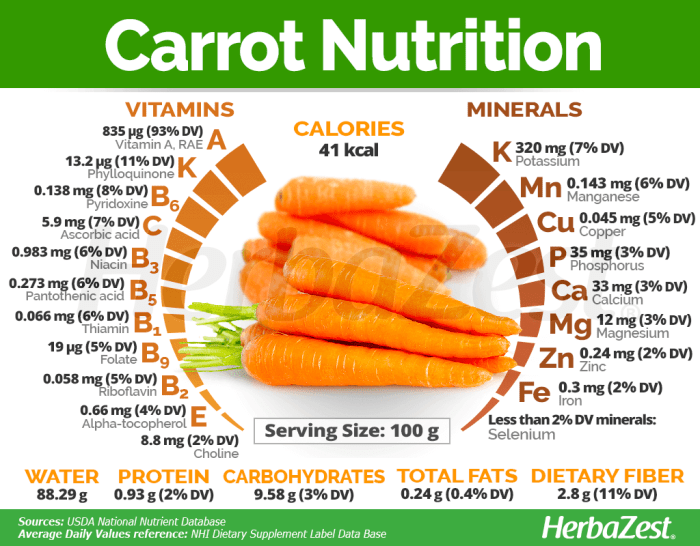
Nutrition facts for a carrot – Carrots, those crunchy orange wonders, are far more than just a rabbit’s delight. They pack a nutritional punch that’s surprisingly potent, offering a delicious way to boost your health. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of carrot nutrition, uncovering the secrets behind their vibrant color and impressive health benefits.
A single carrot boasts impressive vitamin A content, crucial for eye health. However, comparing this to the nutritional profile of breakfast cereals is interesting; for instance, check out the corn flakes nutrition facts to see the difference in fiber and sugar content. Returning to our humble carrot, remember its low calorie count makes it a perfect addition to any healthy diet.
Macronutrient Breakdown in Carrots
Carrots are primarily composed of carbohydrates, with a modest amount of protein and negligible fat. This makes them a relatively low-calorie, energy-boosting snack. The following table provides a detailed breakdown of the macronutrients found in a typical 100g serving:
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g | % Daily Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 9.6g | 3% | grams |
| Protein | 0.9g | 2% | grams |
| Fat | 0.2g | 0% | grams |
*Note: Daily values are based on a 2000 calorie diet and may vary depending on individual needs.*
Micronutrient Profile of Carrots, Nutrition facts for a carrot
Beyond the macronutrients, carrots are brimming with essential vitamins and minerals. These micronutrients contribute significantly to various bodily functions and overall well-being.The impressive micronutrient lineup includes:
- Vitamin A (Beta-carotene): A powerful antioxidant, crucial for eye health, immune function, and cell growth. Beta-carotene is converted into Vitamin A by the body as needed.
- Vitamin C: Another potent antioxidant, vital for collagen production, wound healing, and immune system support. Think of it as your body’s built-in repair crew.
- Vitamin K1: Essential for blood clotting and bone health. It helps prevent excessive bleeding and keeps your bones strong.
- Potassium: An important electrolyte that helps regulate blood pressure and muscle contractions. Keeps your heart happy and your muscles moving smoothly.
- Biotin: Important for cell growth, metabolism, and healthy hair and skin. Contributes to overall cellular function.
Fiber Content and Digestive Impact
Carrots are a good source of dietary fiber, primarily insoluble fiber. This type of fiber adds bulk to your stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. The fiber in carrots also contributes to a feeling of fullness, which can aid in weight management. A 100g serving of carrots provides approximately 2.8g of dietary fiber. Regular consumption of fiber-rich foods like carrots can significantly improve gut health and overall digestive function.
Think of fiber as the friendly janitor of your digestive system, keeping things running smoothly.
Carrots and Health Benefits: Nutrition Facts For A Carrot

So, you’ve learned about the nutritional makeup of carrots – impressive, right? But the real magic lies in what those nutrients do for your body. Think of carrots as tiny, orange superheroes, quietly fighting for your health. Let’s delve into their amazing abilities.
Carrots are bursting with beta-carotene, a pigment that gives them their vibrant orange hue. Your body cleverly converts this beta-carotene into vitamin A, a superstar nutrient crucial for a multitude of bodily functions. This conversion isn’t some alchemic process; it’s a natural, efficient transformation orchestrated by your liver. Think of your liver as a tiny, tireless factory, diligently working to provide your body with the essential nutrients it needs.
Beta-Carotene’s Role in Vision
Vitamin A, derived from beta-carotene, is absolutely essential for maintaining good vision. It plays a critical role in the formation of rhodopsin, a light-sensitive pigment in your retina. Rhodopsin is like the secret ingredient in your eyes’ ability to see in low light conditions. Without sufficient vitamin A, your night vision can suffer, potentially leading to night blindness.
Imagine stumbling around in the dark – not a fun scenario, and easily avoided with a healthy dose of carrots (and other vitamin A-rich foods, of course!).
Antioxidant Properties and Chronic Disease Risk
Carrots aren’t just good for your eyes; they’re also packed with antioxidants. Antioxidants are like tiny bodyguards, protecting your cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can contribute to aging and the development of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer. The antioxidants in carrots help neutralize these free radicals, acting as a shield against cellular damage.
Think of it as a microscopic army protecting your cells from harmful invaders.
Carrots and Heart Health and Immune Function
The benefits of carrots extend beyond vision and antioxidant protection. Studies suggest that the fiber and other nutrients in carrots can contribute to heart health by lowering cholesterol levels. Furthermore, the vitamin A and other immune-boosting compounds in carrots can help strengthen your immune system, making you more resilient to infections. So, not only are carrots good for your eyes, they may also contribute to a healthier heart and a stronger immune response – a true triple threat in the world of healthy eating!
FAQ Corner
Are baby carrots as nutritious as whole carrots?
Generally, yes, but baby carrots often undergo processing (washing, peeling, cutting) which can slightly reduce some nutrient content compared to whole, unprocessed carrots.
Can I eat the carrot greens?
Yes! Carrot greens are edible and contain nutrients such as vitamins A and K. They can be added to salads or cooked like spinach.
How long can I store carrots?
Store carrots in a cool, dark, and dry place. Refrigeration can extend their shelf life, but avoid storing them in the crisper drawer, as the humidity can cause them to spoil more quickly. Properly stored, they can last several weeks.
Are carrots good for weight loss?
Carrots are low in calories and high in fiber, which can contribute to feelings of fullness. They can be a helpful part of a weight-loss diet, but overall calorie intake and balanced nutrition are crucial.
